German steel producer Salzgitter embraces ABB’s electromagnetic stirrer to enhance the efficiency of its new electric arc furnace (EAF) in a groundbreaking move toward hydrogen-based steelmaking.
Salzgitter Flachstahl GmbH, a prominent German steel producer, is set to revolutionize its steelmaking process by transitioning from coal-based to hydrogen-based production. The initiative, part of the SALCOS program, aims to achieve virtually CO₂-free steel production at the company’s Lower Saxony plant by 2033. To realize this ambitious goal, Salzgitter plans to replace existing blast furnaces and converters with three electric arc furnaces (EAFs) and two direct reduction plants. The use of hydrogen is anticipated to result in a remarkable 95% reduction in CO₂ emissions.
ABB, a global technology leader, is playing a pivotal role in this steelmaking transformation. The company is providing Salzgitter with the ABB ArcSave electromagnetic stirrer (EMS), a cutting-edge technology designed to optimize the metallurgical performance of the new EAF supplied by Primetals Technologies. The EAF, known as the Ultimate Furnace, boasts a tapping weight of 220 tons and an annual capacity of 1.9 million tons of steel, marking the initial phase of Salzgitter’s conversion to hydrogen-based steel production.
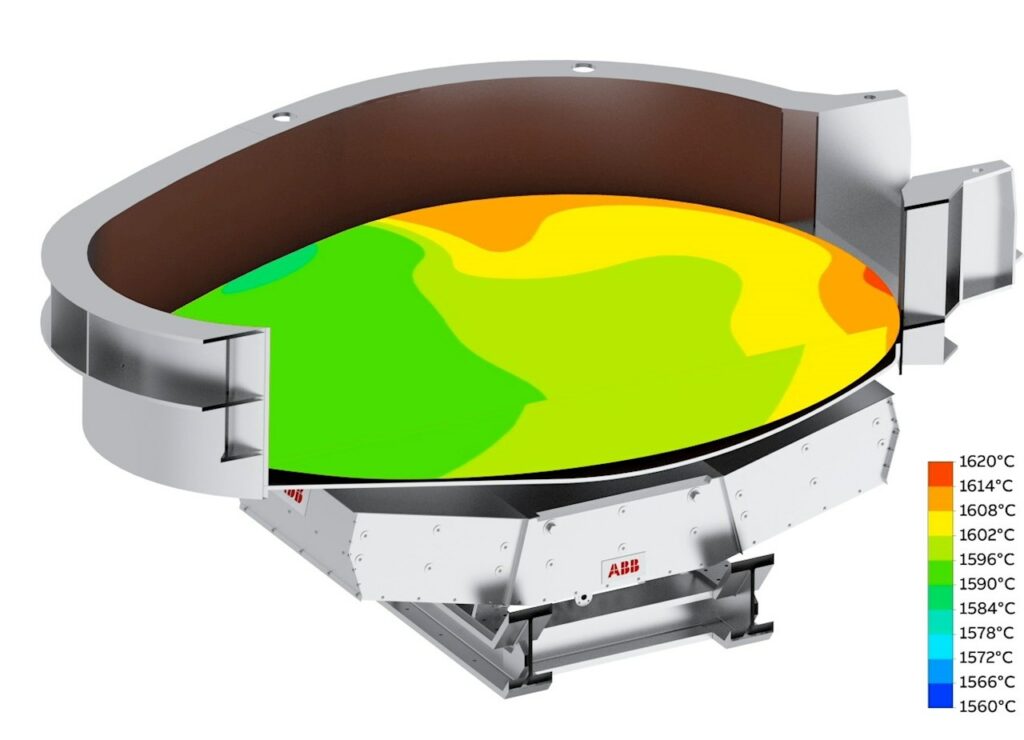
The ABB ArcSave electromagnetic stirrer is a patented EMS technology that promises to enhance metallurgical conditions within the EAF. With over 165 projects globally, this proven technology is set to contribute significantly to Salzgitter’s low CO₂ steelmaking project. The ArcSave technology operates without contact with the bottom of the EAF, employing forced convection to reduce stratification during the melting of large scrap items. This process homogenizes temperature distribution and chemical composition, speeding up the melting of scrap and ferroalloys compared to natural convection alone.
The commissioning of ABB ArcSave at Salzgitter is slated for 2025, aligning with the company’s broader strategy to transition to hydrogen-based steel production. The technology is expected to yield several benefits, including improved yield by approximately one percent, productivity enhancements ranging from five to seven percent, and a reduction in electrical energy consumption by three to five percent. Additionally, ABB’s solution minimizes the need for process additions like alloys and lime, contributing to sustainability goals.