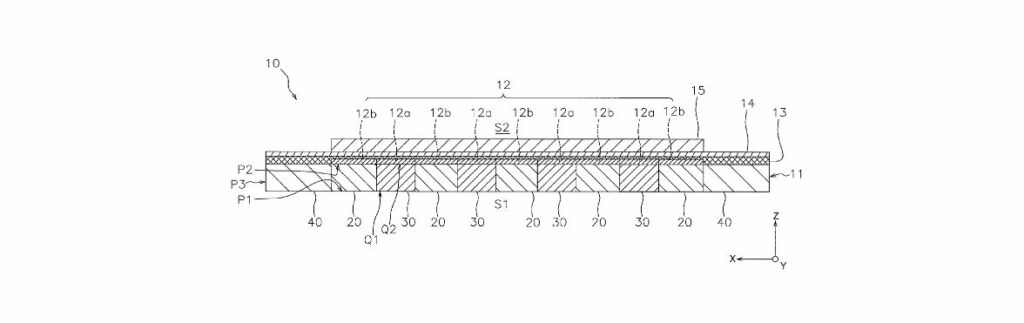
A recent patent, filed on June 13, 2024, by NGK Insulators, Ltd., introduces a novel electrolytic cell designed to enhance hydrogen production. The invention comprises several core components: a support body, a hydrogen electrode active layer, an electrolyte layer, and an oxygen electrode layer. Inventors have also incorporated a hydrogen electrode current collector layer with specially designed beam parts.
Features and Improvements
The patented technology stands out due to its unique hydrogen electrode active layer, which incorporates overlapping and non-overlapping parts about embedded beam parts within the current collector layer. A key innovation lies in the varying particle size of nickel (Ni) particles within these parts. Specifically, the overlap part of the active layer contains Ni particles with a smaller average diameter than the non-overlap part. This differentiation in particle size is expected to improve the overall efficiency and durability of the electrolytic cell.
Potential Applications
This advanced electrolytic cell can be utilized in various hydrogen production processes, specifically in applications where high-efficiency hydrogen generation is critical. Potential use areas include industrial hydrogen production, renewable energy integration, and hydrogen fuel cell technologies. The improved efficiency and durability make it suitable for commercial and large-scale hydrogen production facilities.
Market Impact
Introducing this electrolytic cell could significantly impact the hydrogen market by enhancing the economic viability of hydrogen production. This technology may reduce the overall cost of hydrogen production by improving the efficiency and lifespan of electrolytic cells. This, in turn, could accelerate the adoption of hydrogen as a clean energy source, fostering growth in related industries such as transportation, energy storage, and industrial processes.
Competitive Analysis
The described electrolytic cell offers several competitive advantages over existing hydrogen production solutions. Due to wear and tear on active materials, traditional electrolytic cells often suffer from efficiency losses and decreased durability over time. The innovative use of different particle sizes in the Ni-containing layers addresses these issues, potentially leading to longer-lasting and more efficient electrolytic systems. This could give NGK Insulators, Ltd. a competitive edge in the burgeoning hydrogen market.
Technical Specifications and Methodologies
Key technical aspects of the patent include:
– The support body (11) housing the current collector layer (20)
– The hydrogen electrode active layer (12) with distinct overlap (12a) and non-overlap parts (12b)
– Embedded first and second beam parts (31, 32) that provide structural integrity
– Variation in Ni particle size: smaller average diameter in the overlap part (12a) and larger in the non-overlap part (12b)
These innovations are expected to optimize the electrochemical performance and longevity of the cell.
Key Takeaways
The patent highlights a significant advancement in hydrogen production technology through strategic design changes in the electrolytic cell structure. NGK Insulators, Ltd. aims to provide more efficient and durable solutions in the hydrogen market by incorporating varying particle sizes and robust support elements. If successfully commercialized, this technology could play a pivotal role in reducing the cost of hydrogen production and fostering the transition to a hydrogen-based economy.