A recently filed patent by Bar-Ilan University, dated August 15, 2024, introduces an innovative electrochemical cell apparatus designed to enhance hydrogen production efficiency.
The inventors, associated with the university, have developed a system that significantly differs from existing technologies, presenting potential advancements in the field of hydrogen energy.
Features & Improvements
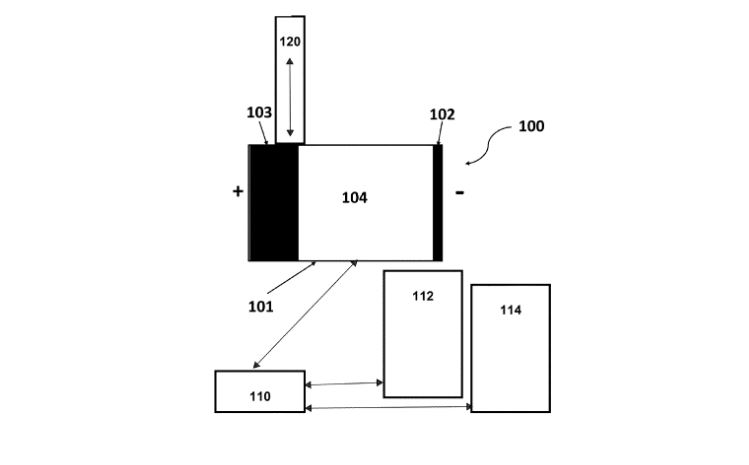
The patented electrochemical cell apparatus features an electrolyte chamber housing both positive and negative electrodes. However, the standout aspect of this design lies in the ratio between the surface areas of these electrodes. Specifically, the surface area of the positive electrode is at least 100 times greater than that of the negative electrode. This significant discrepancy in surface area is a novel approach that could yield high-efficiency rates in hydrogen production by optimizing the electrochemical reactions taking place within the cell.
Potential Applications
The primary application of this patented technology centers around the production of hydrogen fuel. Given the growing global interest in hydrogen as a clean energy source, this electrochemical cell apparatus could play a pivotal role in making hydrogen production more efficient and cost-effective. Additionally, this technology may be utilized in various industrial processes where hydrogen is a key component, such as in chemical manufacturing and energy storage systems.
The patent documentation emphasizes the importance of the ratio between the surface areas of the positive and negative electrodes, which is specified to be at least 100:1. This specific design choice is aimed at maximizing the electrochemical interactions and optimizing hydrogen yield. The electrolyte chamber, containing these electrodes, facilitates the necessary conditions for efficient electrochemical reactions to occur, potentially leading to higher rates of hydrogen production.