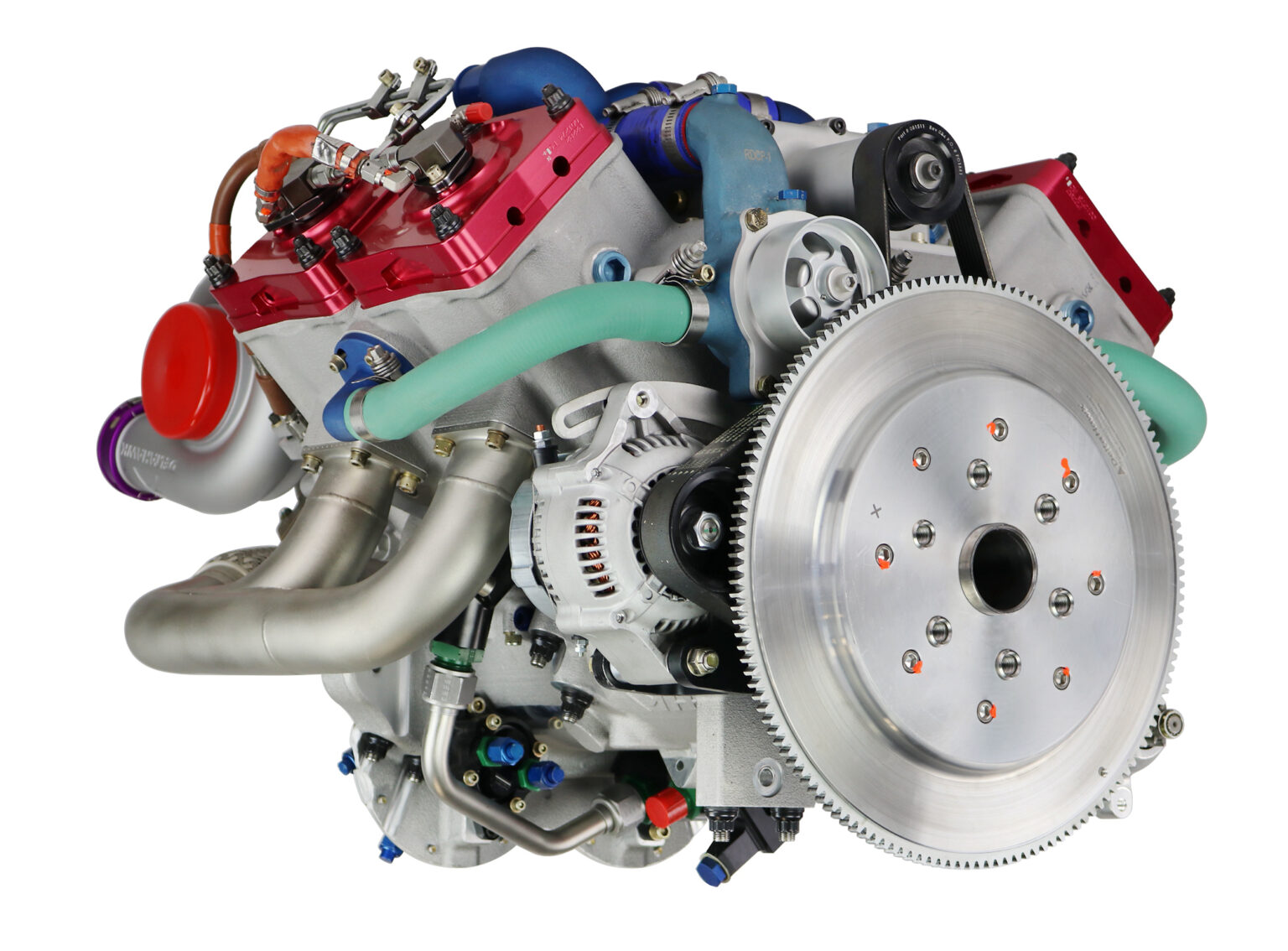
DeltaHawk Engines, renowned for their innovative FAA-certified jet-fueled piston engines, has successfully completed advanced simulation analysis for a hydrogen-fueled variant of its engine family.
This development not only showcases the adaptability of DeltaHawk’s engine architecture but also extends its applications to various markets, including zero-emission vehicles, commercial power solutions, and multiple defense platforms.
DeltaHawk’s primary goal is to revolutionize traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) technology by introducing a hydrogen-powered variant. This move aims to replace more expensive and infrastructure-reliant fuel cell systems, offering higher tolerance for hydrogen impurities and leveraging existing ICE manufacturing expertise and service networks.
The key innovation lies in the use of proven internal combustion engine technology with hydrogen fuel, a shift from the more complex and costly fuel cell systems. The DeltaHawk engine’s adaptable design, based on patented two-stroke technology, proves to be compact, lightweight, and durable – making it an ideal solution for hydrogen fuel. Computer simulations have demonstrated its superiority over legacy four-stroke engine architectures, indicating its potential for widespread adoption.
The advantages of DeltaHawk’s engine design, including reduced development costs, quicker time to market, higher durability, and cost-effectiveness, position it as a catalyst for the rapid adoption of hydrogen power worldwide. With recent global government incentives for hydrogen in commercial trucking, delivery vehicle infrastructure, and military mobility applications, DeltaHawk’s versatile engine family is poised to play a pivotal role in environmental sustainability.