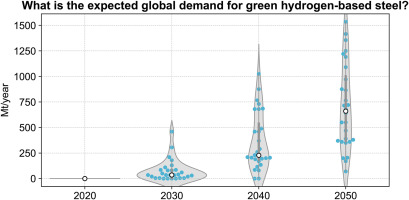
In a new study, researchers Takuma Watari and Benjamin McLellan explore the potential demand for green hydrogen-based steel through a series of 28 scenarios. As the global steel industry grapples with the challenge of reducing its carbon footprint, this research provides critical insights into the role that green hydrogen could play in sustainable steel production.
The growing interest in green hydrogen underscores the relevance of this research as a clean energy solution. The steel industry, a major contributor to global carbon emissions, is under increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable production methods. Green hydrogen, produced using renewable energy sources, offers a promising alternative to conventional, carbon-intensive steelmaking processes.
Main Findings
The study meticulously examines 28 potential scenarios for adopting green hydrogen in steel production. Key findings highlight the varying degrees of demand for green hydrogen-based steel, contingent upon governmental policies, technological advancements, and market dynamics.
– Under optimistic scenarios with strong policy support and rapid technological advancements, the demand for green hydrogen-based steel could grow significantly.
– Conservative scenarios, on the other hand, predict more modest demand increases, influenced by slower technological progress and limited policy interventions.
The findings of this research have profound implications for the steel industry and beyond:
– Steel Production: Green hydrogen can be used as a reducing agent in steelmaking, replacing traditional carbon-based methods and significantly reducing CO2 emissions.
– Energy Sector: Increased demand for green hydrogen-based steel would drive growth in the renewable energy sector, as green hydrogen is produced using wind, solar, or hydropower.
Relevance to the Hydrogen Market
The study’s scenarios offer valuable insights for stakeholders in the hydrogen market. Surging demand for green hydrogen-based steel could stimulate investments in hydrogen production infrastructure and renewable energy projects, creating a symbiotic relationship between the steel and hydrogen industries.
The researchers employed a mixed-methods approach, integrating quantitative modeling with qualitative scenario analysis to project future demand for green hydrogen-based steel. This comprehensive methodology ensures a robust analysis that captures the complexity of the potential market dynamics.
The broader implications of this research are significant for policymakers, industry leaders, and environmental advocates. The transition to green hydrogen-based steel production could be a pivotal step toward achieving global climate goals. Additionally, it underscores the importance of supportive policies and innovative technologies to accelerate the adoption of sustainable practices.
Key Takeaways
– The demand for green hydrogen-based steel is highly variable, dependent on policy, technology, and market factors.
– Green hydrogen presents a viable alternative to traditional steelmaking methods, with substantial environmental benefits.
– The potential growth in demand for green hydrogen-based steel could drive investments in renewable energy, further supporting sustainability goals.
This study offers a clear roadmap for the potential future of green hydrogen in steel production, providing a crucial reference for stakeholders aiming to navigate the evolving landscape of sustainable industry practices.