Plastic waste continues to be a significant environmental challenge globally. A recent patent filed by Borealis AG on June 27, 2024, provides insight into how to address this issue. This article examines the technological advancements, potential applications, market impacts, and competitive landscape associated with Borealis AG’s patented process.
Overview of the Patent
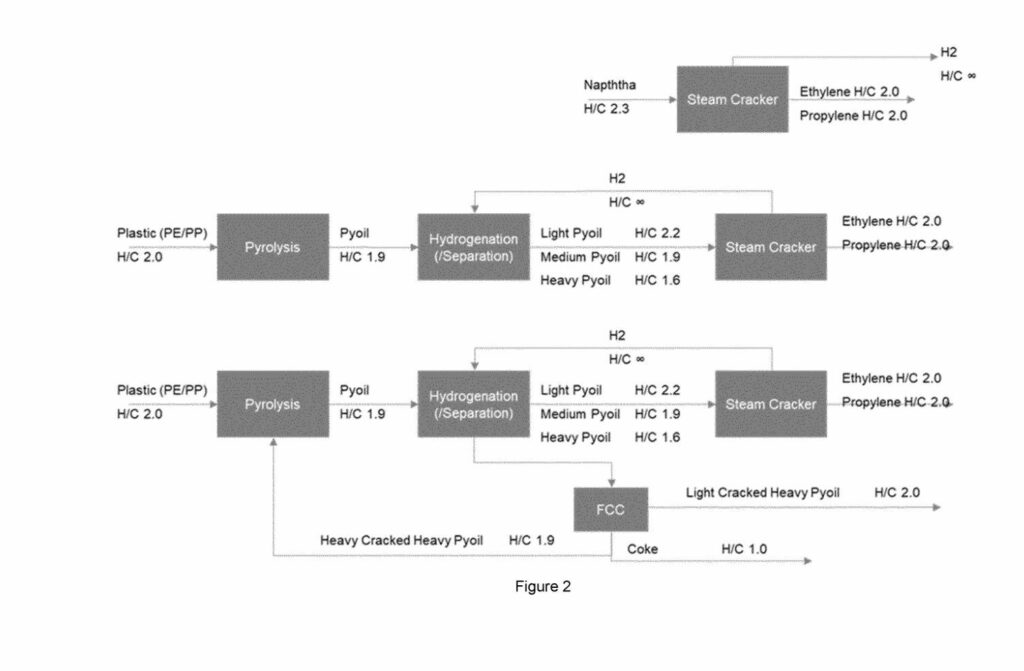
The patent, filed by Borealis AG, details a process for treating mixed plastic waste using a sequence of steps involving pyrolysis, hydrotreatment with hydrogen, and catalytic cracking. The inventors propose a methodology for converting mixed plastic waste into useful fractions, transforming environmental liabilities into valuable resources.
The patent outlines a multi-step process comprising:
1. Converting mixed plastic waste into pyoil using a pyrolysis reactor.
2. Subjecting at least a portion of the pool to hydrogen treatment with a catalyst in a hydro treatment unit to yield a hydrotreated pool.
3. Separating the hydrotreated pyoil into distinct fractions, ideally including light, medium, and heavy fractions.
4. Feeding the heavy fraction into a catalytic cracking reactor to produce a cracked heavy fraction.
This process distinctly integrates hydrogen treatment, which significantly improves the quality of the resultant pyoil by reducing contaminants and enhancing its suitability for further processing.
Potential Applications
The patent describes a hydrotreatment technology that can be instrumental in producing cleaner hydrocarbon fractions from mixed plastic waste. These fractions can be utilized across various industries, such as in producing fuels and chemicals or as feedstock for further refining. This approach contributes to waste management and supports a circular economy by reclaiming valuable resources from plastic waste.
Market Impact
The introduction of this technology could substantially impact the hydrogen and waste management markets. The ability to effectively process mixed plastic waste into high-quality hydrocarbons may drive demand for hydrogen in the hydrotreatment stage, thus expanding its market. Moreover, by converting waste into usable products, this technology can alleviate some pressure on landfills and reduce the environmental footprint of plastic waste.
Competitive Analysis
Compared to plastic waste treatment methods, such as simple pyrolysis or mechanical recycling, Borealis AG’s process offers several advantages. Traditional pyrolysis often results in lower-quality pyoil with higher contaminants. In contrast, integrating a hydrotreatment step in Borealis AG’s method significantly enhances the output quality. Additionally, including catalytic cracking of the heavy fraction can further optimize the breakdown of complex hydrocarbons, which is an improvement over many current technologies that do not fully address the high-molecular-weight components of pyoil.
Technical Specifications and Methodologies
Key technical aspects of the process include:
– Pyrolysis Reactor: Converts mixed plastic waste to pyoil under high-temperature conditions.
– Hydrotreatment Unit: Enhances pyoil quality using a catalyst and hydrogen, removing impurities and stabilizing the hydrocarbon structure.
– Separation Unit: This unit fractionates the hydrotreated pyoil into light, medium, and heavy fractions, enabling targeted downstream processing.
– Catalytic Cracker: Further breaks down heavy hydrocarbon fractions into more valuable, lighter hydrocarbons.