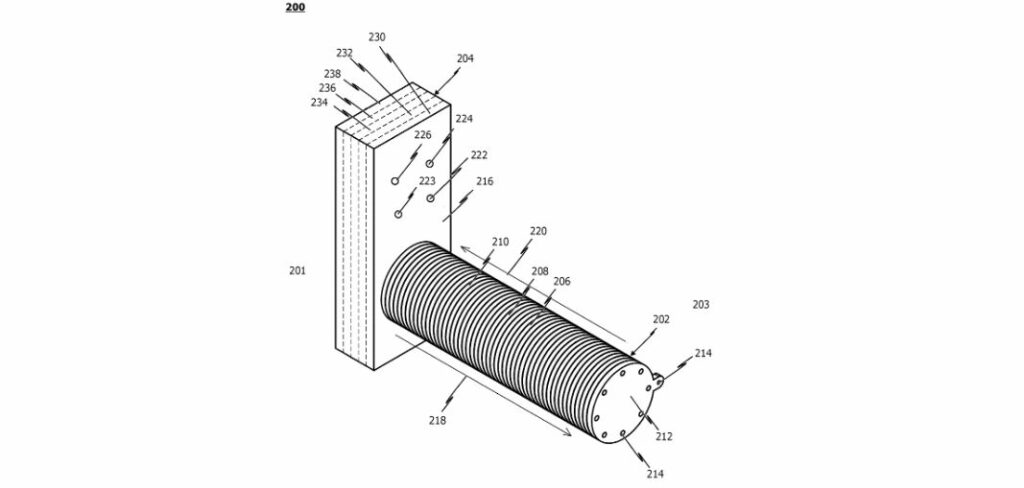
A recent patent titled “Manifold Assembly for an Electrolyser,” filed on June 20, 2024, by inventor Paul Francis Geary, introduces an innovative design to enhance the efficiency of electrolyzers, specifically those used for generating hydrogen from water. The patent details a manifold assembly with a housing block and multiple integrated fluid galleries designed to handle the electrolyte and pressurized process gases the electrolyzer produces.
Unique Features and Improvements
The standout feature of this manifold assembly is its integrated fluid gallery system within a single housing block. This design consolidates the management of electrolytes and process gases, typically handled through separate channels in older systems. By integrating these components, the manifold assembly simplifies the overall design and potentially reduces the risk of leaks and other mechanical failures. The consolidation is expected to streamline the manufacturing process, potentially lowering production costs while improving reliability and performance.
Potential Applications
This patented technology is crucial for hydrogen production processes, an area gaining significant traction as industries seek sustainable energy solutions. Electrolysers using these manifold assemblies can be employed in various sectors, including fuel cell technology, industrial gas production, and even as part of renewable energy storage systems. This manifold assembly’s efficient handling of pressurized gases makes it particularly suitable for large-scale industrial applications where reliability and safety are paramount.
Market Impact
Innovations like this manifold assembly could significantly influence the market with the increasing demand for green hydrogen. By improving the efficiency and reliability of hydrogen production systems, the cost of producing hydrogen may decrease, making it more competitive with traditional fossil fuels. Additionally, the streamlined design could attract manufacturers looking to reduce complexity and improve the scalability of their production lines.
Competitive Analysis
The existing market for electrolyzers features several established technologies, such as polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolyzers and alkaline electrolyzers. This new manifold assembly offers a more integrated and potentially more efficient solution than traditional models. For instance, conventional systems often require extensive external piping and multiple components to manage fluids and gases, increasing the risk of leaks and maintenance issues. In contrast, the integrated design of the new manifold assembly can mitigate these concerns, offering a more compact and robust alternative.
Technical Specifications
According to the patent documentation, the manifold assembly includes integrated fluid galleries marked 110, 122, 128, and 132, which are designed to facilitate the flow of electrolytes and pressurized gases within the system. This integrated approach allows for real-time management and distribution of these fluids, enhancing the electrolyzer’s overall efficiency. The housing block is constructed to withstand high pressures, ensuring safe operation even under demanding conditions.
Key Takeaways
– Innovation: The manifold assembly integrates fluid galleries within a single housing block, simplifying the management of electrolytes and pressurized gases.
– Applications: Suitable for hydrogen production in fuel cells, industrial gas production, and renewable energy storage systems.
– Impact: Potential to lower costs and enhance the efficiency of hydrogen production, making it more viable as a sustainable energy source.
Comparison: It offers a more integrated and reliable alternative to existing electrolyzers, reducing the risk of leaks and maintenance issues.
– Technical Details: This device features specific fluid galleries for optimized management of electrolytes and pressurized gases, ensuring robust and efficient operation.