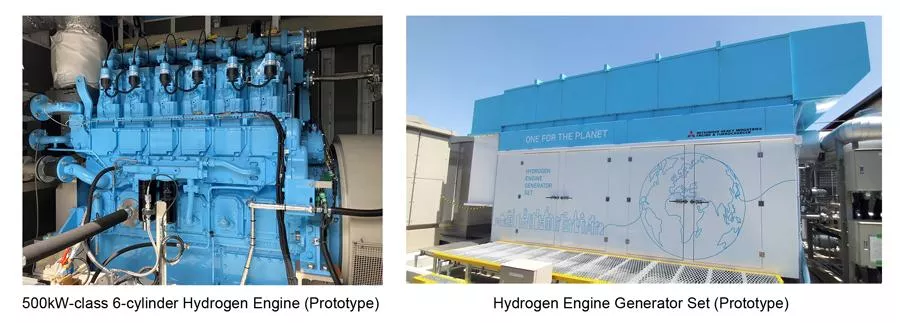
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) has achieved a milestone with the completion of a hydrogen-powered engine generator, poised for in-house testing in Japan. This six-cylinder, 500kW engine will undergo rigorous trials within the fiscal year to evaluate its performance, stability, and reliability under 100% hydrogen load.
MHI’s Engine & Turbocharger (MHIET) division spearheads this ambitious project to confirm the engine’s stability while operating on high-pressure hydrogen. The initial phase of trials will see the engine run on Japan’s city gas before transitioning to pure green hydrogen. This stepwise approach comprehensively evaluates the engine’s capabilities and safety.
The hydrogen-powered engine represents a culmination of extensive research and development by MHIET. The company successfully ran a single-cylinder gas engine cogeneration system in November last year on a 50% hydrogen blend. This success laid the groundwork for the current project, emphasizing the potential of hydrogen in power generation.
The new engine’s design and technological innovations address key challenges in hydrogen combustion, such as flame stability and NOx emissions. By utilizing high-pressure hydrogen, MHIET seeks to optimize combustion efficiency and minimize environmental impact.
Javier Cavada, President and CEO of EMEA at Mitsubishi Power, highlighted the role of hydrogen in grid balancing and energy storage. Despite criticism regarding its use in electricity production, Cavada emphasized hydrogen’s ability to complement other renewable technologies.
Grid balancing is crucial for integrating renewable energy into the power grid. With renewable sources like wind and solar often producing excess energy, hydrogen offers a solution to store and utilize this surplus effectively. Canada noted, “While an area might have 1GW of power demand, the renewables capacity would need to be three times that… hydrogen can definitely take that role and replace the molecule.”