Solid-state batteries are at the forefront of research in energy storage technologies, offering enhanced safety and higher energy densities compared to traditional liquid-based batteries. The recently filed patent by Panasonic Intellectual Property Management Co., Ltd. presents a novel electrolyte composition aimed at advancing solid-state battery technology.
Composition and Components
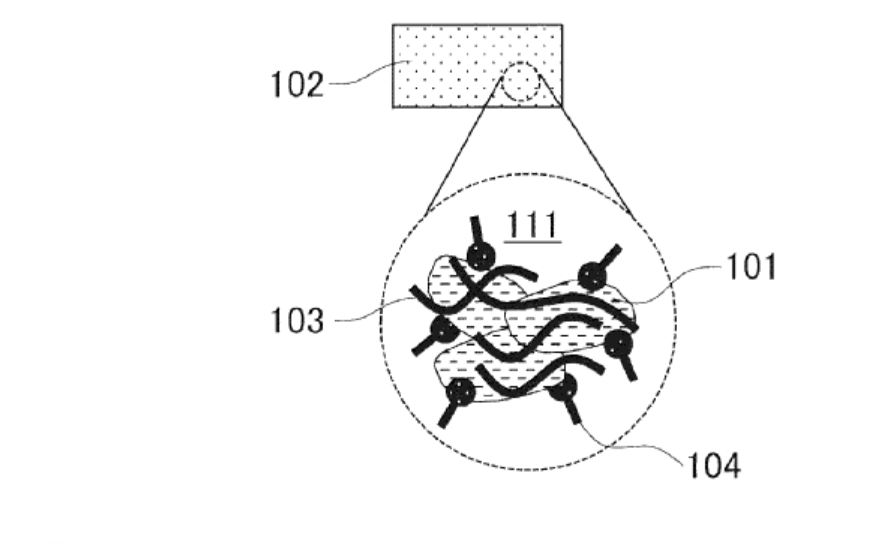
The core of this patented technology lies in its unique electrolyte composition which includes a solvent, an innovative ion conductor, a binder, and a nitrogen-containing organic substance. The ion conductor is composed of a solid electrolyte that specifically includes sulfide structures. A notable aspect of the composition is the binder, which utilizes a styrenic elastomer. This enhances the flexibility and integrity of the solid electrolyte layer, potentially contributing to improved battery performance and longevity.
Chemistry Behind the Innovation
The nitrogen-containing organic substance in this patented composition is highlighted by its formula: it features diverse R groups, indicating that it can be optimized or tailored for specific performance features. For instance, R1 and R4 create a broad range of possibilities for customization, being either chain alkyl groups or chain alkenyl groups, thus allowing the composition to be engineered for specific battery characteristics. Furthermore, the variability in R2 enhances the chemical stability and robustness of the electrolyte, which is crucial in commercial applications.
Potential Applications and Impact
One of the significant challenges for solid-state batteries has been achieving reliable ion conductivity while maintaining structural integrity under diverse conditions. By using a sulfide-based solid electrolyte coupled with an adaptable nitrogen-containing organic substance, this patent offers a promising solution. It aims to bridge the gap between high theoretical performance and actual practical utility, making solid-state batteries more viable for commercial applications.
While this patent does not claim immediate market transformations, its contributions could yield incremental advancements in battery technology. It reflects the broader industry ambition to optimize solid-state battery capabilities and underscores efforts to reduce dependency on liquid electrolytes. The successful implementation of such innovative compositions could eventually lead to smaller, lighter, and more efficient batteries for a variety of applications, from consumer electronics to electric vehicles.
In summary, the filed patent for a solid electrolyte composition from Panasonic Intellectual Property Management Co., Ltd. offers a glimpse into the future of energy storage solutions. By focusing on chemical innovation and electrolyte stability, this patent takes a strategic step towards overcoming some of the intrinsic challenges of solid-state battery technology, hinting at a future where these batteries become more commonplace and impactful across different markets.