A patent titled “Hydrogen Storage Material Including Metal-Organic Frameworks,” filed on June 27, 2024, by LG Chem, Ltd., introduces a novel method for hydrogen storage. The inventors, whose specific names aren’t in the abstract, propose an advanced organic light-emitting device with unique compounds designed to enhance hydrogen storage efficiency.
Features and Improvements
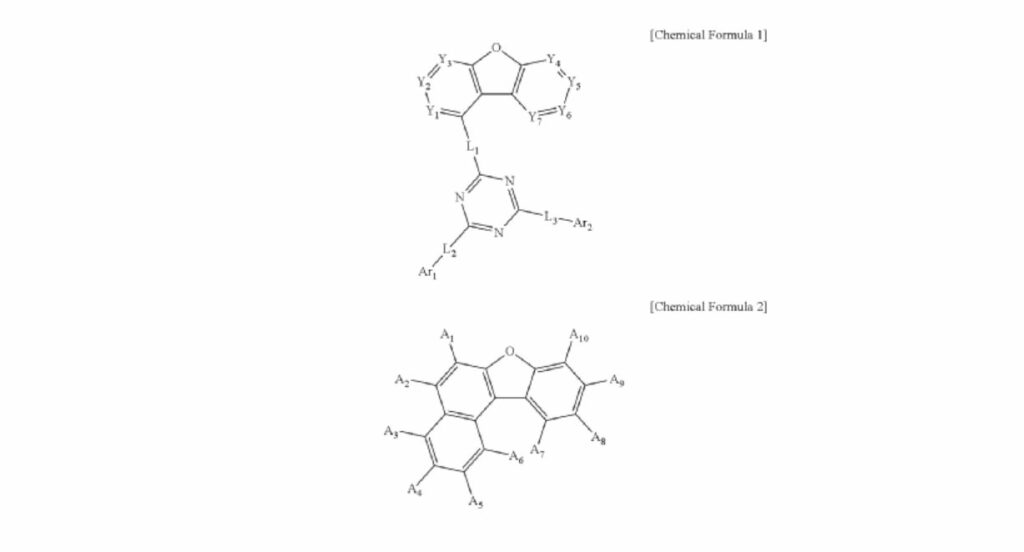
This patent revolves around an organic light-emitting device, explicitly featuring a light-emitting layer composed of two chemical compounds: Chemical Formula 1 and Chemical Formula 2. The key innovation lies in the precise molecular structure. The light-emitting layers consist of substituted and unsubstituted aryl and heteroaryl groups, each containing vital heteroatoms such as nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur. This structure significantly elevates the hydrogen storage capabilities compared to existing technologies.
Potential Applications
This patented technology’s primary application is in hydrogen storage systems. With the global push towards cleaner energy, efficient hydrogen storage is becoming increasingly crucial. This technology can be applied across various sectors, such as automotive, where hydrogen fuel cells are a growing alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. Moreover, potential applications extend to power generation and portable electronic devices, providing a lighter, more efficient energy storage solution.
Market Impact
Introducing such an advanced hydrogen storage material could considerably impact the hydrogen market. Enhanced storage efficiency addresses one of the significant hurdles in hydrogen fuel adoption. By improving storage technology, hydrogen becomes a more viable mainstream energy source, potentially leading to increased market investments and accelerated development in related technologies.
Comparison with Existing Solutions
Current hydrogen storage solutions often suffer from low storage density and high operational costs. While functional, traditional metal hydrides and high-pressure gas tanks lack the efficiency and cost-effectiveness required for widespread adoption. The patented technology from LG Chem, Ltd. promises to outperform these traditional methods by providing higher storage densities at potentially lower costs, making it a competitive alternative in the market.
Technical Specifications
The patent describes a meticulous process involving intricate chemical formulations represented by Chemical Formula 1 and Chemical Formula 2. Noteworthy specifications include:
– The use of C6-60 aryl or C2-60 heteroaryl groups.
– Incorporation of heteroatoms like N, O, and S to enhance chemical stability and storage properties.
– Substituents such as hydrogen or deuterium in various configurations (A1 to A10) contribute to the compound’s stability and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
The innovative hydrogen storage material developed by LG Chem, Ltd. offers a promising advancement in the hydrogen storage domain. Key takeaways include:
– Significant improvements in storage efficiency over existing technologies.
– Broad potential applications across automotive, power generation, and portable electronics sectors.
– A positive market impact by potentially lowering costs and increasing hydrogen storage density.
– Advanced technical specifications that contribute to the superior performance of the storage material.
This patent underscores an essential step towards advancing hydrogen as a sustainable and economical energy solution, marking a notable milestone in the clean energy landscape.