The patent describes an innovative method and device for the production and storage of hydrogen through a process known as heterogeneous catalytic electrolysis.
This method utilizes a unique combination of materials and technological processes to efficiently generate hydrogen gas from water, whether it be freshwater or seawater.
Hydrogen is a key element in the transition towards cleaner energy sources, and its production and storage is a critical area of research. The method outlined in this patent offers a new approach to generating hydrogen using a technique called heterogeneous catalytic electrolysis. This process leverages specific materials and configurations to improve efficiency and effectiveness in hydrogen production.
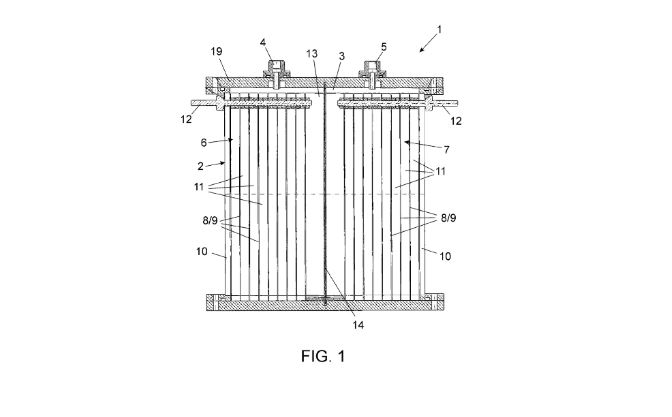
Central to this method are the electrodes, which play a crucial role in the electrolysis process. The electrodes described in this patent have a unique structure composed of a porous substrate, preferably activated carbon. This is crucial for facilitating the necessary chemical reactions. Moreover, these electrodes are coated with a semiconductor layer made of oxides, nitrides, or hydroxides of transition metals. Titanium dioxide is particularly favored for its properties.
An important aspect of this technology is the specific energy band configuration of the semiconductors used. The valence band energy level is notably designed to be substantially below the oxidation potential of water. Conversely, the conduction band energy level is above the reduction potential of hydrogen concerning the standard hydrogen electrode. This strategic positioning of energy bands allows for efficient hydrogen generation.
The method enables both dynamic and static hydrogen generation. Dynamic generation refers to the continuous production of hydrogen, while static generation involves simultaneous production and storage of hydrogen. The latter is achieved by using electrodes that also serve as storage devices due to their cumulative electronic capacitance. This dual functionality is a significant advancement in the field of hydrogen technology.
Stay updated on the latest in energy! Follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook, and X for real-time news and insights. Don’t miss out on exclusive interviews and webinars—subscribe to our YouTube channel today! Join our community and be part of the conversation shaping the future of energy.