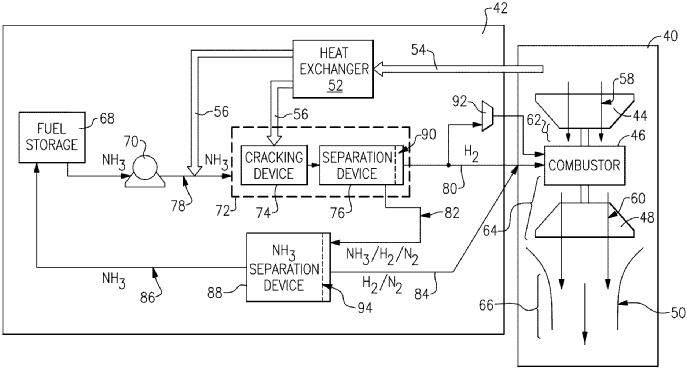
This patent covers an innovative gas turbine engine system developed by RTX Corporation. The engine features a decomposition device that breaks down ammonia into components rich in hydrogen, along with a separation device to isolate the hydrogen from the residual gases.
This hydrogen is then used in the combustor to generate gas flow more efficiently. The core innovation lies in the engine’s ability to decompose ammonia into hydrogen and other residual gases. The cracking device is crucial here, designed to optimize this breakdown process. More hydrogen than ammonia is produced, making it a more efficient fuel source for the turbine engine.
After the initial decomposition, a separation device further isolates the hydrogen from the remaining ammonia and nitrogen. This separation process ensures that the hydrogen flow is maximized, improving the engine’s overall combustion efficiency and reducing waste.
The combustor is engineered to utilize the separated hydrogen flow. By specifically designing the combustor to handle hydrogen as the primary fuel, the engine can achieve a higher efficiency compared to standard turbines that rely on traditional fuels.
The engine also includes a compressor section that supplies the combustor with compressed air. This compressed air is critical for maintaining optimal combustion temperatures and efficiencies. Additionally, the turbine section is designed to be in communication with the gas flow from the combustor, ensuring a seamless flow of energy throughout the system.
This patented gas turbine engine offers several advantages, including increased fuel efficiency and reduced emissions due to the use of hydrogen. Its potential applications range from power generation to aviation, where efficient and environmentally friendly energy solutions are highly sought after.