GOLDWIND SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. has filed a patent for a novel ammonia production system that promises a more efficient and potentially eco-friendly alternative to conventional methods.
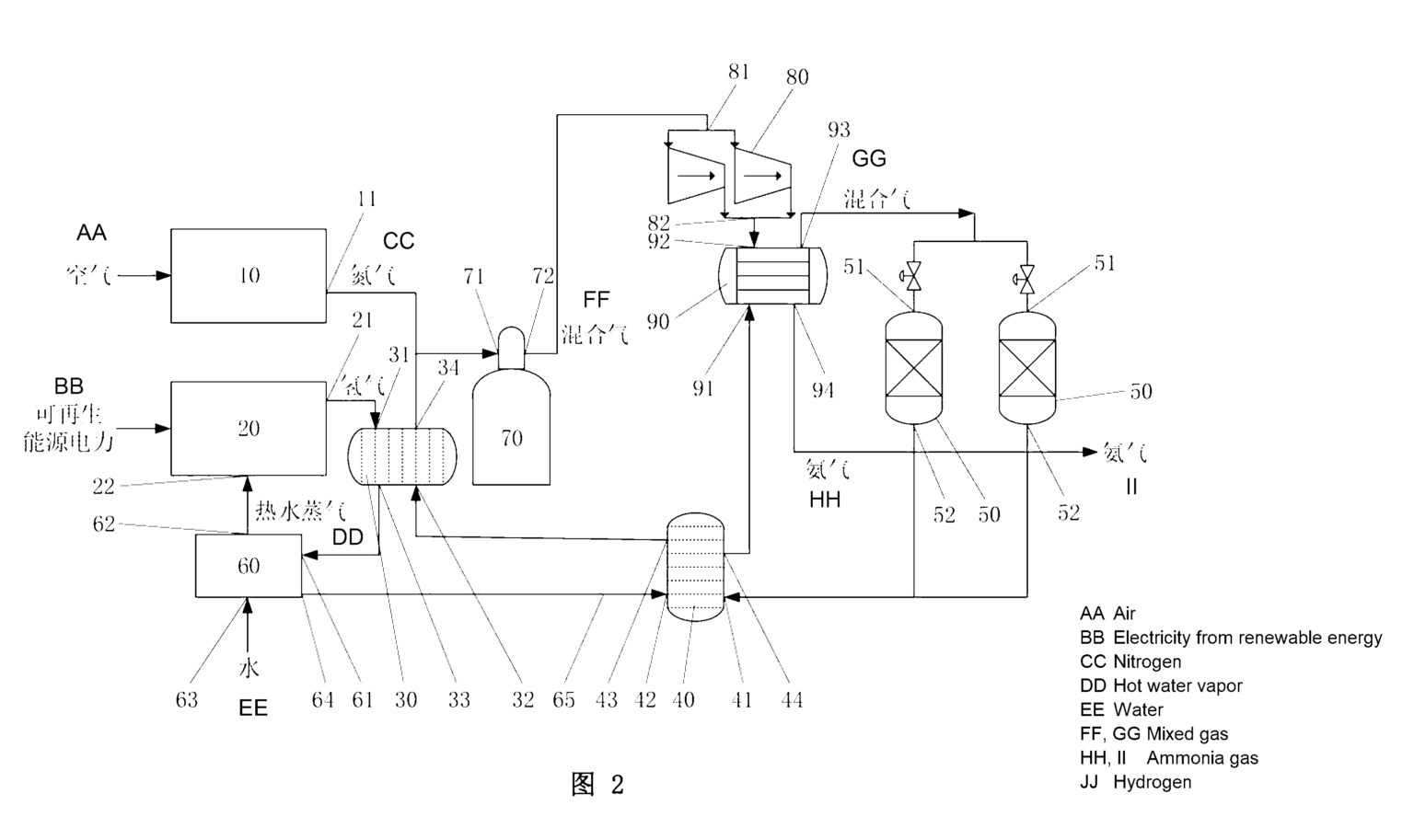
The patent outlines a system comprising several key components that work synergistically to produce ammonia. These include a nitrogen production device, a solid oxide electrolytic cell, a synthesis column, and a heat storage device. Here’s a closer look at each:
1. Nitrogen Production Device
This device is responsible for preparing nitrogen, crucial for ammonia synthesis. It features a nitrogen outlet through which nitrogen is supplied to the system. This component ensures a steady flow of nitrogen, which is necessary for the following stages of synthesis.
2. Solid Oxide Electrolytic Cell
A standout feature of this system is the solid oxide electrolytic cell. It prepares hydrogen by utilizing water vapor, a process that is both efficient and sustainable. The hydrogen produced here is a primary reactant in the ammonia synthesis process. Notably, the cell includes a hydrogen outlet through which the hydrogen is discharged to proceed to the synthesis column.
3. Synthesis Column
The synthesis column is where the magic happens. This component is equipped with a gas inlet and an ammonia gas outlet. Here, the previously produced nitrogen and hydrogen mix and react under controlled conditions to synthesize ammonia gas. This efficient synthesis mechanism is key to the system’s overall effectiveness.
4. Heat Storage Device
The heat storage device adds a layer of energy efficiency to the system. Featuring a heat storage medium, the device absorbs the heat discharged during the processes within the hydrogen outlet and/or the ammonia gas outlet. The stored heat is then utilized to heat water vapor, which is reintroduced into the solid oxide electrolytic cell for hydrogen production. This recycling of heat optimizes energy usage and reduces waste, aligning with sustainable production goals.
While not claimed as revolutionary, this patent introduces a method that optimizes energy use and leverages more sustainable raw materials in ammonia production. This system could be particularly beneficial for industries looking to reduce their carbon footprint and reliance on nonrenewable energy sources.