Siemens Energy Global GmbH & Co. KG has filed a patent for an ingenious system that harnesses the power of offshore wind turbines to produce and store energy.
This system takes advantage of the dynamic nature of open water environments to offer a versatile solution in energy generation and management. Here, we delve into the key components and concepts highlighted in the patent.
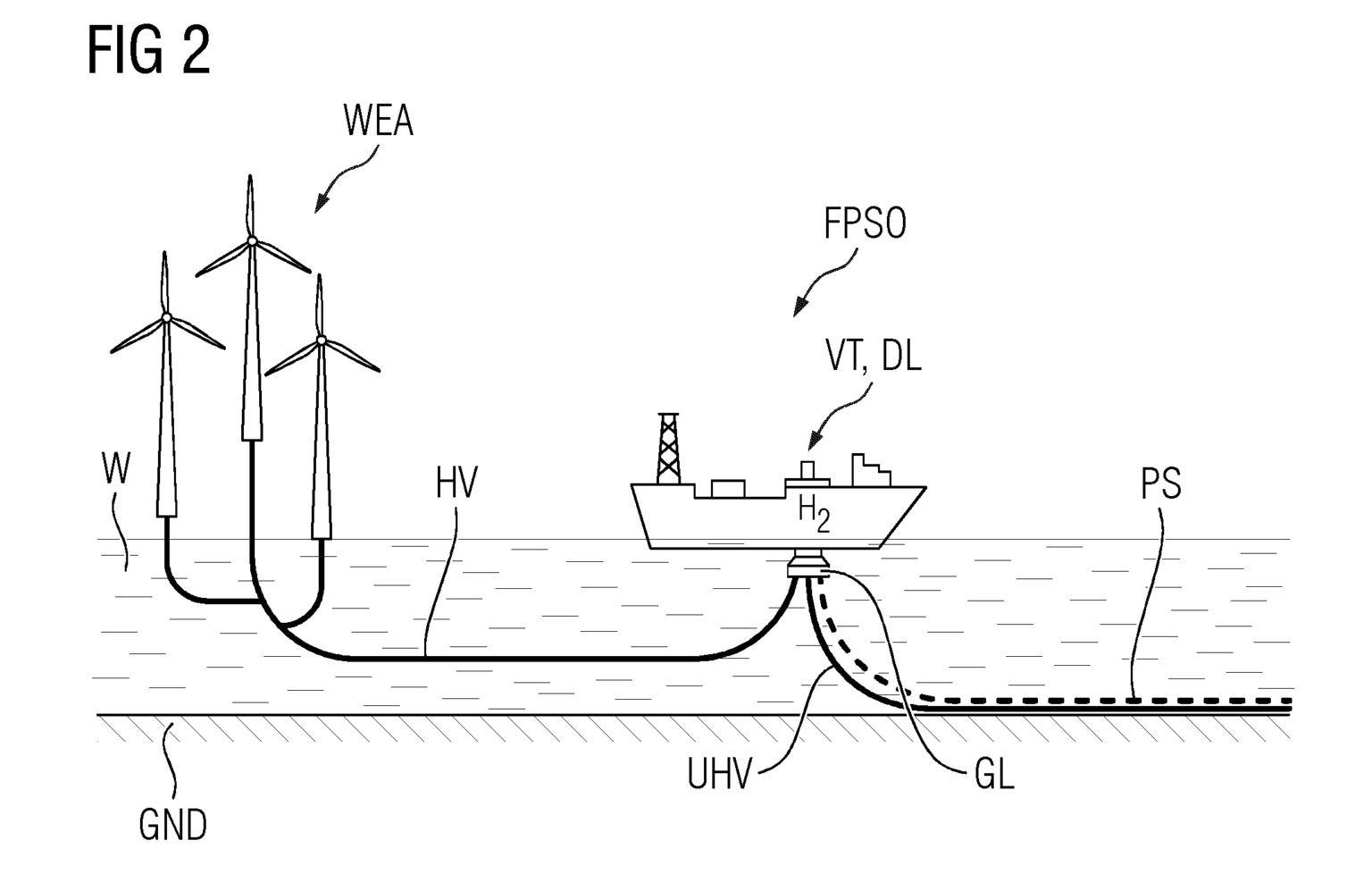
Central to this patent is the offshore wind turbine, referred to as WEA, that forms the core of the system. Unlike typical installations, this turbine is specifically designed to be releasably connected to a marine vehicle, the FPSO (Floating Production, Storage, and Offloading vessel). This innovative connection allows for more flexible operation, enabling the system to adapt to varying environmental conditions and operational demands.
The marine vehicle comes equipped with a transformer device, identified as TR, which converts electrical voltage to accommodate both low and high demands. This transformation is crucial for efficient energy management and application. Coupled with this is an electrolysis device, labeled ES, which utilizes the electrical energy to produce hydrogen gas (H2) through electrolysis. The generated hydrogen is then stored in a designated tank, denoted as T, also located within the marine vehicle.
This patent emphasizes the system’s ability to shift dynamically between different operating modes, including energy storage and transmission. By effectively balancing between these modes, the system ensures energy availability and reliability. This adaptability is further enhanced by incorporating redundancy and maintainability into the design, reducing downtime and operational risks.