Air Liquide filed a patent dated June 27, 2024, titled “A Method and Apparatus for Producing Hydrogen in a Steam Methane Reformer with Reduced Carbon Emissions.” The patent focuses on a novel method for producing hydrogen while significantly decreasing carbon emissions, a critical advancement in the quest for sustainable energy solutions.
Features and Improvements
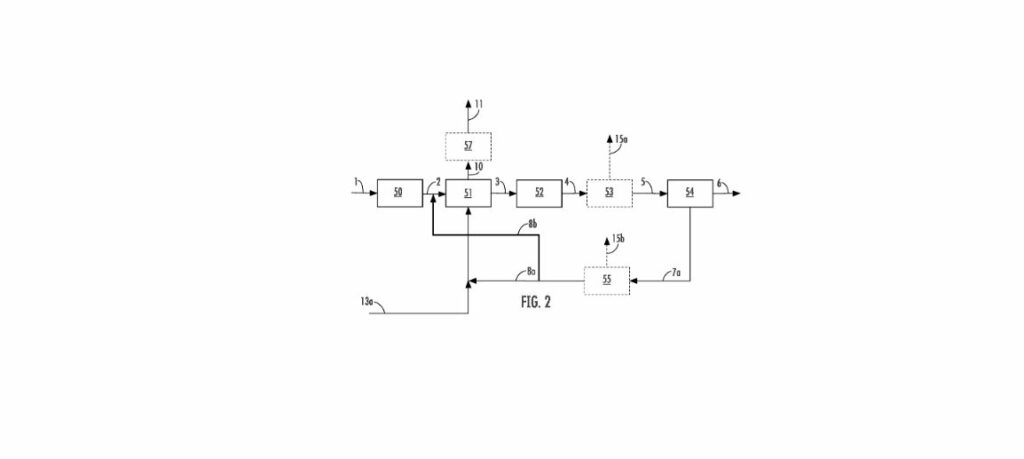
This patent introduces an innovative process that combines steam methane reforming (SMR) with advanced carbon emission reduction techniques. One of the most noteworthy features is the combustion of ammonia as a fuel, coupled with a hydrogen fuel stream and an oxidizer. This process not only supports the catalytic conversion of methane but also produces flue gas with lower carbon content than traditional methods.
Additionally, including a shift conversion unit helps convert carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide and hydrogen, thereby increasing the hydrogen yield. The technology also emphasizes a meticulous purification process to produce a high-purity hydrogen product stream.
Potential Applications
The primary application of this patented technology lies in hydrogen production facilities aiming to minimize their carbon footprint. This could be particularly beneficial for industries requiring large hydrogen volumes, such as oil refining, chemical manufacturing, and metal processing. Furthermore, this technology could be instrumental in supporting the hydrogen economy by providing greener hydrogen for fuel cells used in transportation and power generation.
Market Impact
This patent has the potential to significantly impact the hydrogen market by offering a more sustainable and cost-efficient method of hydrogen production. As the world increasingly shifts towards lower-carbon solutions, industries adopting this technology could benefit from reduced emissions, qualifying for carbon credits, and complying with stringent environmental regulations.
Competitive Analysis
This patent stands out compared to existing hydrogen production technologies due to its focus on reducing carbon emissions. Traditional SMR processes are generally effective but are criticized for their high carbon output. By integrating ammonia combustion and a sophisticated purification system, this innovation not only curtails emissions but also enhances hydrogen yield.
Other technologies, such as water electrolysis, offer zero-emission hydrogen but often at higher operational costs and energy requirements. Thus, this patented method could strike a balance by offering a relatively cleaner and more economically feasible solution in the interim phase.
Technical Specifications and Methodologies
The key steps in this patented process are:
1. Heating a feed stream containing methane to over 500°C using a first heat exchanger.
2. Introducing this heated feed stream into a reaction zone for catalytic conversion, producing a reformed stream comprising hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and unreacted methane.
3. Utilizing a shift conversion unit to convert the reformed stream in the presence of steam, resulting in a shifted gas stream with hydrogen and carbon dioxide.
4. Purifying the shifted gas stream to isolate the hydrogen product stream and tail gas.
5. Heating the reaction zone through the combustion of ammonia and hydrogen fuel in the presence of an oxidizer, thus generating a flue gas.
Key Takeaways
Air Liquide’s patent represents a significant advancement in hydrogen production technology by successfully integrating methods to reduce carbon emissions. The use of ammonia in the combustion process and an efficient shift conversion unit stands out as a unique approach that offers environmental benefits without compromising productivity. As industries continue to seek greener alternatives, this innovation is poised to play a pivotal role in transforming the hydrogen market.