Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells (SOEC) are devices utilized for electrolysis of water, leading to the production of hydrogen, a much-needed clean energy source. They operate at high temperatures and promise high efficiency, which is critical for large-scale industrial applications.
The New SOEC Module
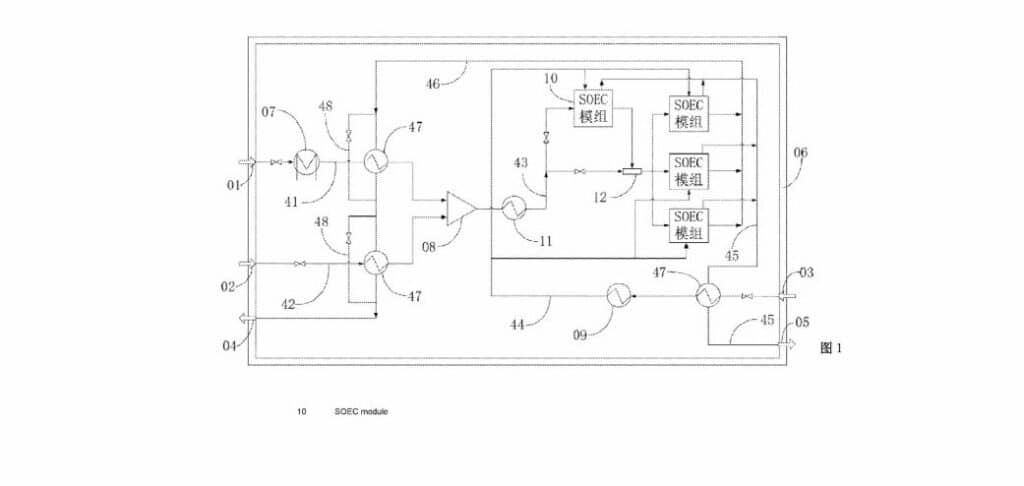
The patent introduces an advanced SOEC module aimed at optimizing hydrogen production through an innovative design based on a multi-stack-core module. The core innovation lies in its arrangement of multiple electrolytic cell stack cores within a heat preservation shell, ensuring efficient thermal management and electrochemical performance.
Component Breakdown
The device comprises several key components, each playing a crucial role in the overall functionality. The steam generator is responsible for providing the steam necessary for the electrolysis process, while the mixer ensures that it is properly combined with other elements. An air heater is included to regulate the temperature of the air before it enters the system.
SOEC Module Features
Each SOEC module within the device is designed with several specific inlets and outlets. These include a hot air module inlet, a hydrogen-containing mixed steam module inlet, an oxygen-rich air module outlet, and a product crude hydrogen module outlet. This design enables a highly controlled and efficient flow of materials and reactions within the module.
The Electrolytic Cell Stack Core
Central to the patent is the electrolytic cell stack core within the preservation shell. Each core has its own inlets and outlets, including a hot air single-stack inlet, a hydrogen-containing mixed steam single-stack inlet, and corresponding outlets for oxygen-rich air and crude hydrogen. This modular approach is key to scaling the process and optimizing hydrogen yield.
While the significance of the patent shouldn’t be overstated, the introduction of a multi-stack-core module in SOEC technology represents a noteworthy progression in the field of hydrogen production. The design improvements could potentially lead to increased efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and lower costs, contributing to more sustainable and economically viable hydrogen production processes.
The patent on the SOEC module and water electrolysis hydrogen production device underscores the ongoing advancements in clean energy technology. As the demand for hydrogen as a green fuel continues to grow, innovations such as these could play a significant role in meeting global energy needs while reducing environmental impact.