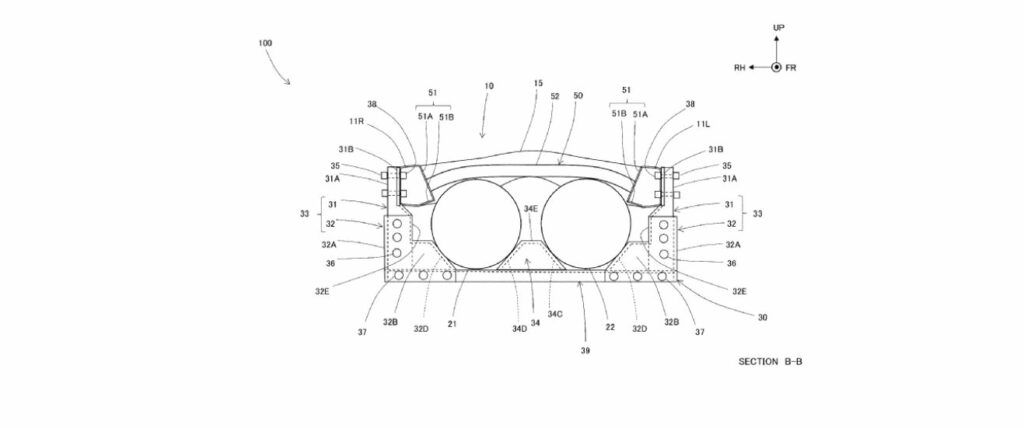
Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha has filed a new patent highlighting an advanced fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) design. The patent delineates a structure comprising a pair of side rails running longitudinally along the vehicle, a lower cross member connecting these rails, a hydrogen tank mounted on this lower structure, and an upper cross member linking the rails above the hydrogen tank.
Features and Improvements
This new setup introduces several distinct features to enhance the structural integrity and safety of the FCEV’s hydrogen storage system. The strategic placement of the hydrogen tank between the upper and lower cross members offers improved stability and protection. Essentially, the dual-layer cross-member configuration provides a robust framework, potentially minimizing damage in the event of a collision and safeguarding the hydrogen tank from external impacts.
Potential Applications
This patented technology is primarily tailored for use in fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), a segment gaining traction as the automotive industry pivots toward sustainable energy solutions. The robust design can be applied to various vehicle models, ensuring safe and efficient hydrogen storage across different FCEV platforms.
Impact on the Hydrogen Market
The introduction of this advanced hydrogen storage solution could significantly influence the hydrogen market. This innovation may accelerate consumer adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles by bolstering the safety and reliability of FCEVs. Increased market confidence in the safety of hydrogen storage could also stimulate investments in hydrogen production, distribution infrastructure, and associated technologies.
Competitive Analysis
Comparatively, existing FCEVs employ hydrogen storage solutions often integrated under the vehicle’s floor or within the rear compartment. While these designs have demonstrated safety and efficiency, Toyota’s patented double cross-member framework introduces an added layer of protection. This distinctive approach could offer Toyota a competitive edge by potentially setting higher safety benchmarks in the market.
Technical Specifications and Processes
The patent outlines a detailed structural arrangement where:
1. The side rails extend longitudinally along the vehicle.
2. A lower cross member spans the vehicle’s width below these rails.
3. The hydrogen tank is securely mounted on this lower cross member.
4. An upper cross member connects the side rails above the hydrogen tank, creating a protective enclosure.
Implementing these specifications will make the vehicle’s frame notably more resilient, potentially reducing the likelihood of hydrogen tank damage during accidents.
Summary of Key Takeaways
Toyota’s patent presents a well-engineered solution to enhance hydrogen tanks’ safety and structural integrity in fuel-cell electric vehicles. The innovative cross-member design not only ensures better protection for the hydrogen tank but also suggests a potential step forward in elevating the market standards for FCEV safety. As the industry moves toward greener transportation solutions, such advancements are crucial in fostering broader acceptance and trust in hydrogen-powered vehicles.