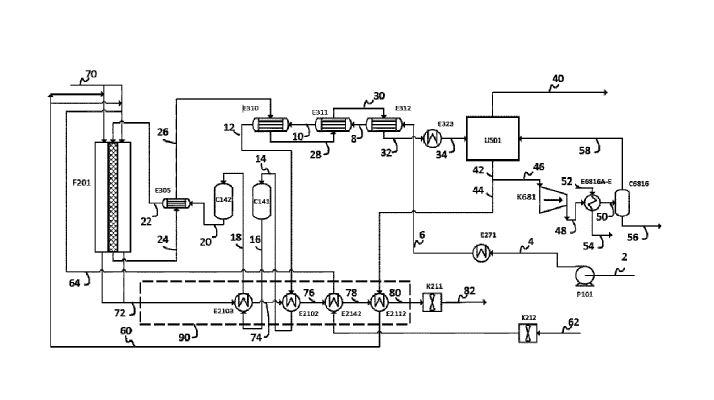
A recent patent filed by Air Products and Chemicals introduces a novel process and apparatus for cracking ammonia, aiming to improve hydrogen production efficiency.
The patent outlines a process where heated ammonia gas at super-atmospheric pressure undergoes catalytic cracking in an adiabatic reaction unit to produce a partially cracked ammonia gas. This partially cracked gas is then fed into catalyst-containing reactor tubes in a furnace, resulting in further cracking and the production of a gas mixture consisting of hydrogen, nitrogen, and residual ammonia.
Unique Features and Improvements
One of the standout features of this patented technology is its efficient heat integration. The process utilizes heat exchange with the cracked gas to provide the necessary thermal energy for heating the partially cracked ammonia gas. This method significantly optimizes energy consumption, ensuring a more efficient and sustainable hydrogen production process.
Potential Applications
The technology described in the patent has significant potential applications, particularly in the hydrogen production sector. The process can be integrated into existing hydrogen production facilities to enhance efficiency or be employed in new installations aimed at producing hydrogen more sustainably. Additionally, industries dependent on hydrogen, such as fuel cells, ammonia synthesis, and various chemical