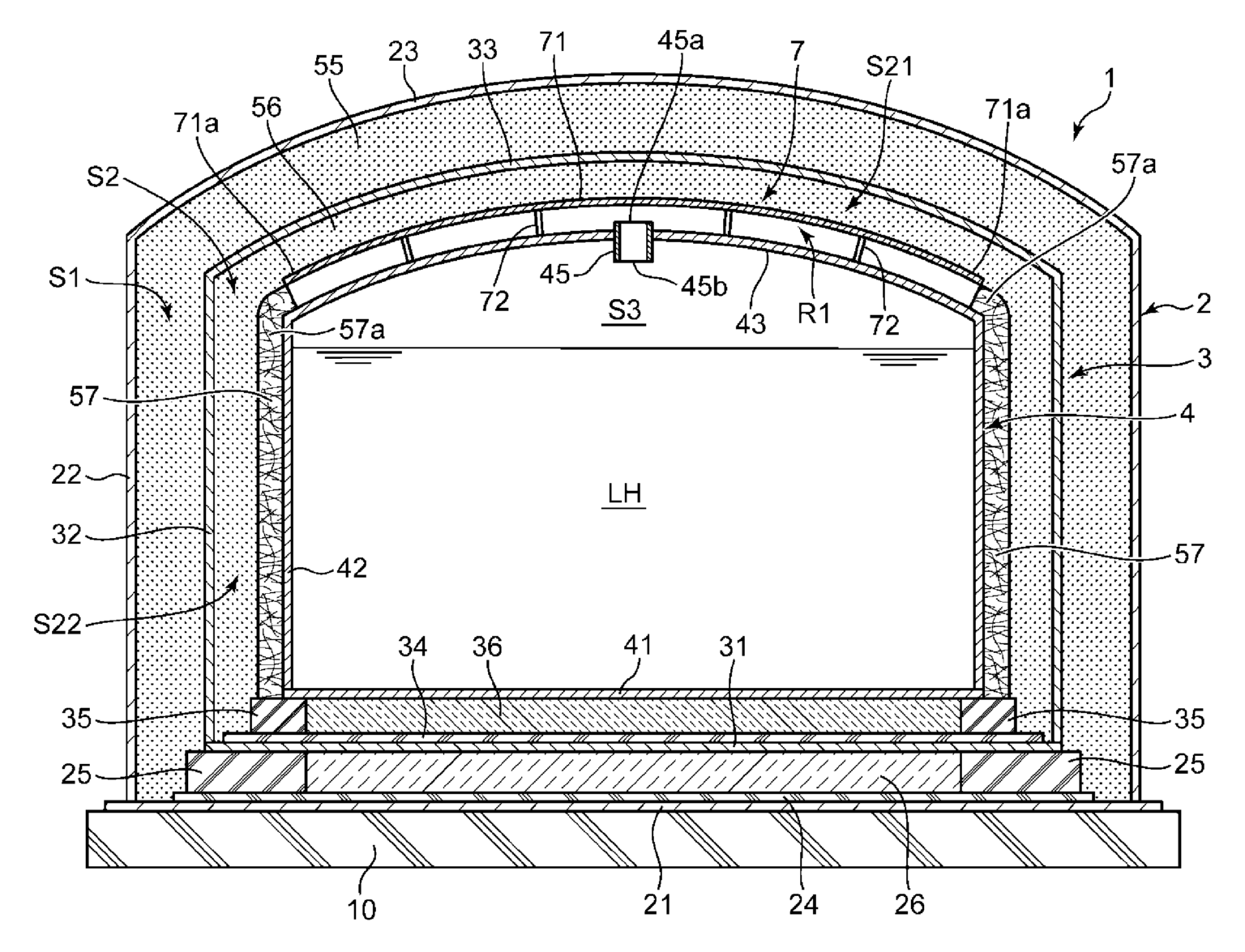
The patented liquefied hydrogen storage tank introduced by Kawasaki Heavy Industries stands out due to its advanced insulation and innovative structural design.
The storage system utilizes a multi-layered tank approach featuring an inner tank, an intermediate tank, and an outer tank. These layers are critical for maintaining the low temperatures necessary for hydrogen in its liquid state, which boils at only 20.28 K (−252.87°C).
Significantly, the patent describes a heat-insulating space that includes specific roof and side peripheral partitions. This design compartmentalizes the space between the inner and intermediate tanks into a roof space part and a side peripheral space part, each filled with a heat-insulating material to minimize thermal conduction. There is also a communication pipe that aids in gas circulation between these compartments, ensuring a stable thermal environment within the storage tank.
Potential Applications
Hydrogen storage technology is crucial for industries transitioning toward greener energy solutions. This particular storage tank holds potential applications in various sectors:
1. Renewable Energy: Ensuring reliable hydrogen storage for energy generated from renewable resources like solar and wind.
2. Transportation: Supporting hydrogen-fueled vehicles by providing efficient storage solutions for refueling stations.
3. Industrial Use: Facilitating the storage of hydrogen for processes in chemical manufacturing and other industrial applications.
The introduction of this advanced storage solution could significantly impact the hydrogen market by addressing one of its primary challenges—efficient and safe storage of hydrogen in liquid form. Reliable storage technology is essential for the widespread adoption of hydrogen as a clean energy source. This innovation could accelerate the development and deployment of hydrogen infrastructure, thereby fostering market growth and adoption.