The patent filed by Kawasaki Jukogyo Kabushiki Kaisha introduces an innovative approach to the storage of liquid hydrogen, a crucial component in various industrial applications and emerging hydrogen economies.
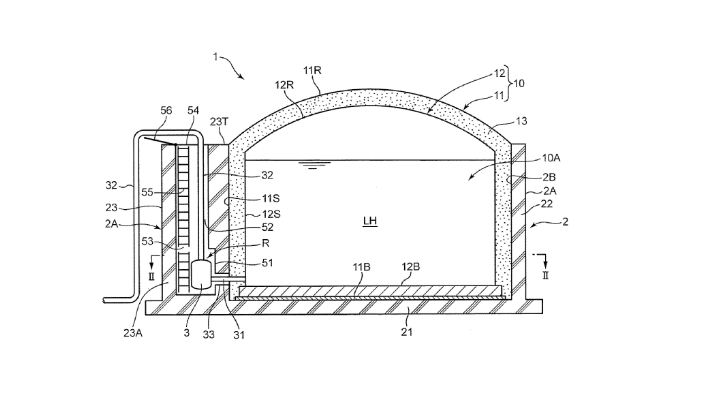
The patented design outlines a liquid hydrogen storage tank comprised of several key components: a tank body, a dike, a pump, and a housing chamber. Each of these elements plays a pivotal role in enhancing the tank’s functionality and safety.
The tank body is designed with an inner and outer tank. The inner tank is responsible for creating the storage space required for keeping liquid hydrogen. This is insulated with a thermal layer to maintain the temperature necessary for hydrogen’s liquid state. Surrounding this is the outer tank, which adds an additional layer of protection and insulation.
Integral to the storage system is the dike, which features both outer and inner peripheral surfaces. The inner surface contacts the side plate of the outer tank, forming a secure barrier. This dike is strategically designed to rise upward and encircle the outer periphery of the tank body, ensuring any accidental spills are contained and mitigating potential hazards.
A standout feature of this design is the integrated pump system. The pump facilitates the discharge of liquid hydrogen from the inner tank through its side plate to the outside, ensuring efficient and controlled release of hydrogen as needed. To protect this vital component, a housing chamber is positioned between the dike’s outer peripheral surface and the storage space. This placement not only secures the pump but also contributes to the streamlined design of the storage system.
Stay updated on the latest in energy! Follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook, and X for real-time news and insights. Don’t miss out on exclusive interviews and webinars—subscribe to our YouTube channel today! Join our community and be part of the conversation shaping the future of energy.