The Institute for Advanced Engineering has recently filed a patent for a low-carbon emission hydrogen extraction system. The patent, which was filed on June 20, 2024, introduces several innovative features aimed at enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of hydrogen production.
Overview of the Patent
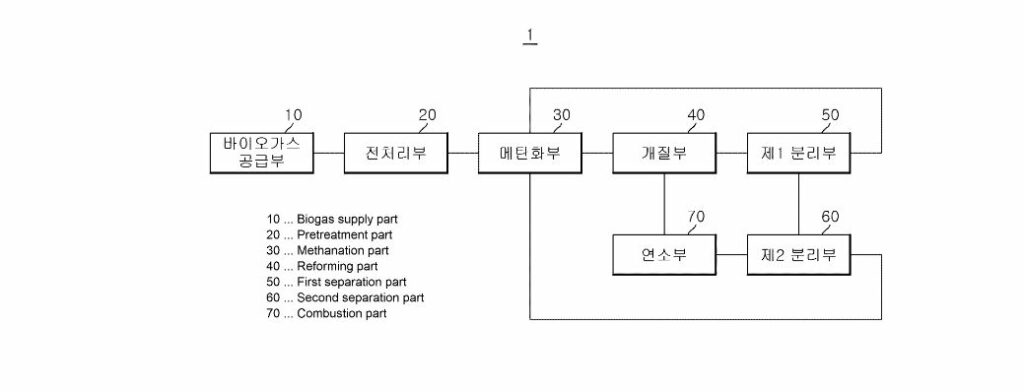
The patented system comprises several key components: a biogas supply part, a methanation part, a reforming part, a first separation part, and a second separation part. These components work in a coordinated manner to produce hydrogen with minimal carbon emissions. The biogas supply part is designed to store and provide biogas, which is then methanized in the methanation part. Methane produced in this step is reformed in the reforming part, producing reformated gas. This gas is subsequently separated to extract hydrogen in the first separation part, and the off-gases containing carbon dioxide are further processed in the second separation part.
Unique Features and Improvements
One of the primary advancements presented in this system is its integrated approach to biogas methanation and hydrogen extraction. Unlike conventional hydrogen production methods, which often result in significant carbon dioxide emissions, this system captures and reuses some carbon dioxide in the methanation process. This closed-loop method minimizes emissions and improves the overall efficiency of hydrogen production.
Potential Applications
The low-carbon emission hydrogen extraction system has a wide range of potential applications. It can be utilized in industries that require substantial hydrogen supplies, such as chemical manufacturing, refining, and fuel cell production. Additionally, the system could be implemented in renewable energy projects where biogas is readily available, promoting sustainable energy sources.
Market Impact
If commercialized, this patent could significantly impact the hydrogen market by providing a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional hydrogen production methods. As the demand for clean energy solutions rises, the technology could pave the way for more sustainable industrial practices. It also aligns with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints, enhancing its attractiveness to stakeholders aiming for greener operations.
Competitive Analysis
Compared to existing hydrogen extraction solutions, this patented system stands out for its efficient carbon dioxide recapture and reuse. Traditional hydrogen production methods, such as steam methane reforming (SMR), often lead to high carbon dioxide emissions without recapture mechanisms. The new system’s ability to minimize emissions presents a noteworthy advancement, potentially giving it a competitive edge in the clean energy market.
Technical Specifications
The system’s technical specification includes its ability to store and supply biogas efficiently, methanize carbon dioxide, and reform the resulting methane. The first and second separation parts are critical in optimizing the purity of the hydrogen produced and the recapture of carbon dioxide. Such integration of processes ensures high efficiency and sustainability.
Summary
The Institute for Advanced Engineering patent introduces a low-carbon emission hydrogen extraction system that integrates biogas methanation, methane reforming, and gas separation processes. This approach enhances the efficiency of hydrogen production and significantly reduces carbon emissions. Potential applications include various industrial sectors and renewable energy projects, with a notable impact expected in the clean energy market. By effectively competing against traditional methods, this innovative system could set new standards for environmentally friendly hydrogen production.