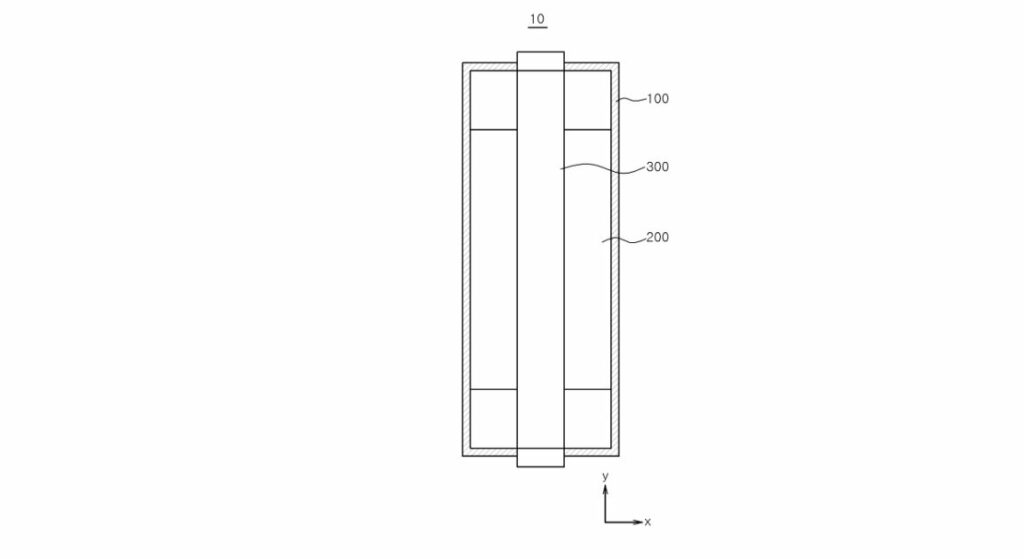
The patent introduces a revolutionary carbon dioxide methanation apparatus designed to achieve low-carbon hydrogen production.
The apparatus comprises two main components: a methanator and a reformer, both integrated into a reactor main body.
1. Methanator: This component efficiently carries out the carbon dioxide methanation reaction from one side to the other of the reactor’s main body.
2. Reformer: Positioned either inside or outside the methanator, the reformer utilizes the heat generated by the methanator to trigger its reforming reaction.
This novel heat-exchange mechanism between the methanation and the reformer is designed to optimize energy efficiency, thus reducing carbon emissions in hydrogen production.
Potential Applications
1. Hydrogen Fuel Production: The apparatus can significantly enhance the efficiency and sustainability of hydrogen fuel production.
2. Industrial Chemical Processes: Industries that require hydrogen for processes like ammonia synthesis or metal refining could benefit from reduced carbon footprints.
3. Energy Storage Solutions: The apparatus can be integrated into renewable energy systems to store excess electricity as hydrogen.
Compared to existing solutions, the patented technology offers:
– Enhanced Energy Efficiency: The dual-component system ensures better utilization of reaction heat.
– Lower Carbon Emissions: The Apparatus Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Optimizing the Methanation and Reforming Reactions.
– Flexibility in Design: The reformer can be placed inside or outside the methanator, offering versatility in different industrial settings.
Existing technologies often involve separate units for methanation and reforming, leading to higher energy consumption and increased operational expenses.
Technical Specifications
1. Reactor Main Body: Designed to extend from one side to the other, serving as the primary structure for the methanation and reforming reactions.
2. Methanator: Positioned within the reactor main body, carrying out carbon dioxide methanation.
3. Reformer: Heat from methanation is also utilized within the reactor’s main body to reform methane.
Key Takeaways
1. Integration of Processes: The apparatus combines methanation and reforming in a single unit, enhancing energy efficiency and lowering emissions.
2. Versatile Configuration: This configuration allows for flexible placement of the reformer, making the system adaptable to various industrial environments.
3. Market Implications: Promises a more sustainable and cost-effective hydrogen production process, aligning with global trends towards cleaner energy solutions.