A patent recently filed by Subsea 7 Norway AS outlines an innovative design for a subsea unit intended for the storage of hydrogen gas underwater.
This concept leverages key principles of underwater construction and hydrogen storage, promising efficient and safe containment of hydrogen at depth.
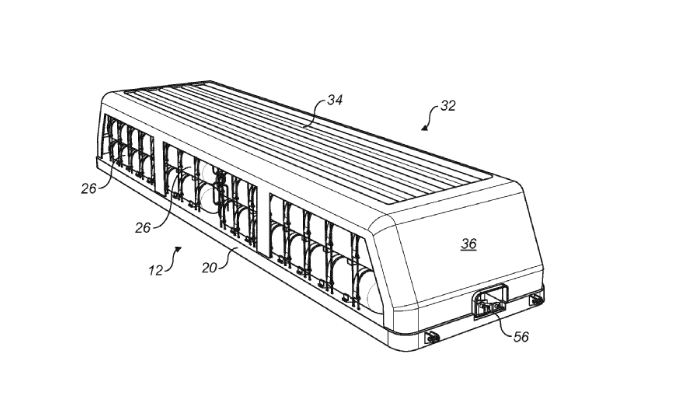
The patented design features a weighting base on which an array of interconnecting storage tanks is mounted. The base, which can be constructed from concrete, provides the necessary stability to counteract the buoyant forces that act on the tanks when submerged. The base can be cast from concrete on the deck of a vessel, allowing for ease of assembly and deployment before being launched into the water.
A critical component of the design is a protective structure fixed to the base, covering the array of tanks. This structure serves to shield the tanks from external impacts and environmental factors that could compromise their integrity. Additionally, a series of strap restraints are employed to secure the tanks against buoyant upthrust. These restraints curve over the top of each tank, ensuring that the tanks remain firmly anchored to the base.
Restraints are connected to elongate tensile members that extend upwardly from the base, positioned on opposite sides of each tank. This arrangement efficiently transfers the loads from each tank to the base, without imposing unnecessary stress on the tanks themselves. The clever design of this load path not only enhances the structural stability of the storage unit but also optimizes the efficiency with which stresses are managed across the system.
The development of subsea hydrogen gas storage units has significant implications for the energy sector. As hydrogen becomes an increasingly viable alternative to fossil fuels, the ability to store large quantities safely and efficiently becomes paramount. This subsea unit offers a promising solution, allowing for the offshore storage of hydrogen in areas where renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, are harnessed. The deployment of such technology could facilitate a scaling up of hydrogen production and storage, thus supporting broader efforts to transition to renewable energy sources.
Stay updated on the latest in energy! Follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook, and X for real-time news and insights. Don’t miss out on exclusive interviews and webinars—subscribe to our YouTube channel today! Join our community and be part of the conversation shaping the future of energy.