The concept of lighter-than-air crafts, revitalized with contemporary technology, is the subject of a patent recently filed by ZeroAvia.
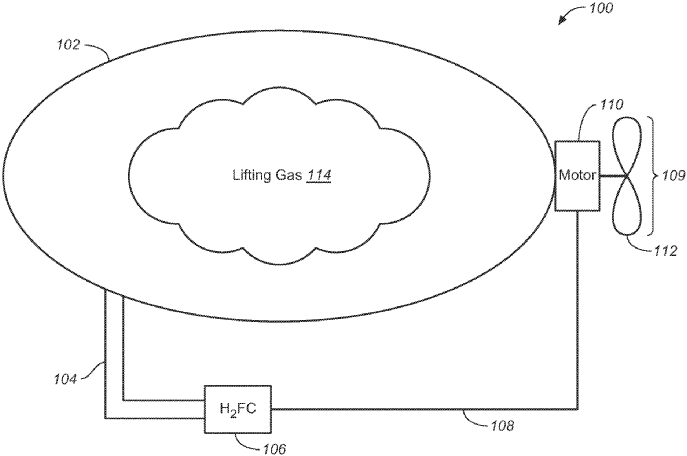
This innovation is centered around an airship design that harnesses hydrogen not only as a lifting gas but also as a fuel source. A sophisticated hydrogen fuel cell is integral to the design, promising advancements in the fields of sustainability, efficiency, and safety. In this article, we’ll explore the key features and implications of this noteworthy patent.
Traditionally, lighter-than-air crafts have relied on helium for buoyancy. However, ZeroAvia’s design partially replaces helium with hydrogen, which plays a bifurcated role. Not only does hydrogen provide the necessary lift, but it also fuels the craft’s propulsion through a linked hydrogen fuel cell. This dual-functionality of hydrogen is central to the airship’s innovative design, potentially offering significant cost reductions and performance efficiencies.
The incorporation of hydrogen fuel cells represents a significant advancement over previous technologies. In this design, the fuel cell is fluidically coupled with the airship’s interior hydrogen supply, allowing for the continuous generation of electricity. This electricity powers the propulsion system, offering the possibility of quieter and more environmentally friendly travel compared to traditional fuel-powered engines.
Safety has always been a critical concern when discussing hydrogen, known for its flammable nature. ZeroAvia addresses this by incorporating an inerting gas system. This system utilizes exhaust from the hydrogen fuel cell, mixing it in specific ratios with the lifting gas to ensure the resultant mixture is nonflammable during flight operations. This inerting approach is key to mitigating the risks associated with hydrogen, making the airship design not only innovative but also safe for widespread use.
The propulsion system integrated into the envelope of the airship is capable of delivering sufficient thrust for navigating and maneuvering through the air. By combining traditional lighter-than-air benefits—such as low operating costs and the ability to hover—with these modern propulsion technologies, the craft promises versatility across various use cases, including cargo transport and passenger travel.
Stay updated on the latest in energy! Follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook, and X for real-time news and insights. Don’t miss out on exclusive interviews and webinars—subscribe to our YouTube channel today! Join our community and be part of the conversation shaping the future of energy.