A recent patent granted to NIHON NOHYAKU outlines a novel hydrogen storage system leveraging advanced metal hydrides.
This technology promises improvements over existing solutions by enhancing the efficiency, safety, and capacity of hydrogen storage.
Unique Features and Improvements
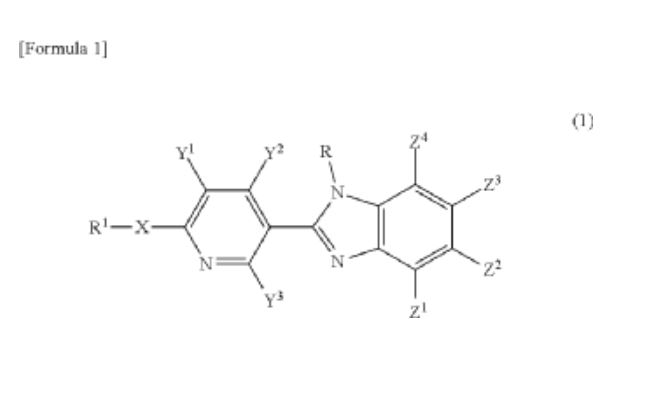
This patent introduces a benzimidazole compound, as represented by the general formula (1). The compound facilitates more efficient hydrogen storage by optimizing the chemical interactions necessary for hydrogen absorption and desorption.
Key features include:
– Improved Hydrogen Absorption Rate: The chemical composition ensures a faster and more efficient absorption rate, addressing one of the critical limitations of current hydrogen storage systems.
– Safety Enhancements: The hydrogen storage system reduces risks associated with high-pressure storage by utilizing solid-state hydrides.
– Increased Storage Capacity: By optimizing the material properties, the system can store a higher density of hydrogen in a smaller volume.
Potential Applications
The technology described in the patent has diverse applications in industries where hydrogen is emerging as a crucial energy carrier. These applications include:
– Automotive Industry: The improved efficiency and safety of hydrogen storage can accelerate the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
– Renewable Energy Storage: This technology can be used to store hydrogen generated from renewable sources, thereby providing a stable and long-term energy storage solution.
– Industrial Processes: Hydrogen is a critical component in various industrial processes, and this storage system could enhance operational efficiency.
The introduction of an advanced hydrogen storage system could significantly influence the hydrogen market by addressing some of the key technical challenges associated with hydrogen storage. The improved storage capacity and safety could lead to wider adoption of hydrogen-based technologies across multiple sectors.