Joby Aero, Inc. recently filed a patent for a hydrogen-powered aircraft with a sophisticated fuel cell system to enhance propulsion efficiency, titled “Aircraft with Hydrogen-Powered Fuel Cell System.”
Features and Technological Improvements
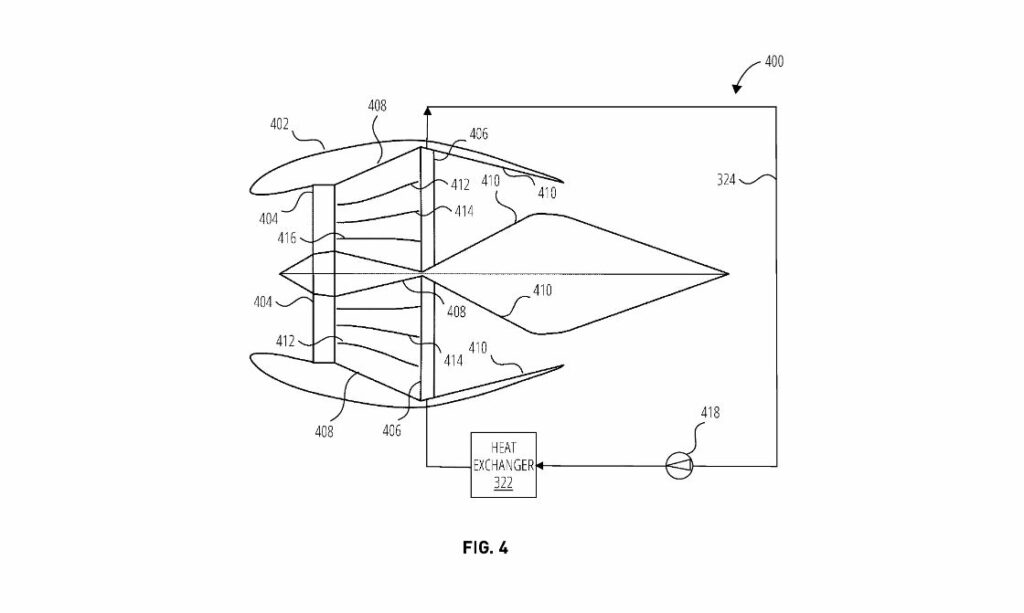
The core innovation in the patent involves an integrated fuel cell system (designated as 300) powered by hydrogen. A standout feature is the inclusion of dual heat exchangers designed to manage thermal regulation and propulsion efficiency. Specifically, a first heat exchanger (322) transmits heat from the fuel cell to a coolant fluid within a coolant loop. The second heat exchanger (406) leverages this heat, transferring it from the coolant fluid to the air passing through a conduit in the propulsion unit. This dual heat exchange process not only cools the fuel cell efficiently but also heats the airflow in the propulsion unit, thereby enhancing the system’s overall efficiency.
Potential Applications
This patent primarily addresses aviation applications that require efficient thermal management and optimized propulsion. Hydrogen fuel cells are known for their clean energy output, which can significantly reduce aircraft carbon footprint. This technology could be instrumental in commercial aviation, air taxis, and even unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Market Impact
Joby Aero could lead to more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly aircraft. As the aviation industry seeks to comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, such innovations could have a considerable market impact.
Comparison with Existing Solutions
The patented technology offers several advantages over traditional jet engines and even current electric propulsion systems. Conventional engines are not as efficient in thermal management and often have higher emissions. While cleaner, Current electric propulsion systems may not achieve the same efficiency level in heat exchange and propulsion. Joby Aero’s dual heat exchanger system uniquely handles the dual challenge of cooling the fuel cell while increasing propulsion efficiency, which is not seen in existing market solutions.
Technical Specifications and Processes
The process involves a conduit through which air is propelled, aided by a carefully designed fuel cell system. The first heat exchanger directly interfaces with the coolant fluid from the fuel cell, while the second heat exchanger, located in the propulsion unit conduit, heats the air by transferring heat from the coolant fluid. This ingenious process ensures the fuel cell remains within optimal operating temperatures and enhances the propulsion unit’s efficiency by using the otherwise wasted heat energy.
Key Takeaways
– Patent Overview: “Aircraft with Hydrogen-Powered Fuel Cell System,” filed by Joby Aero, Inc. on July 4, 2024.
– Core Innovation: Dual heat exchangers that optimize thermal management and propulsion efficiency in a hydrogen-powered aircraft.
– Applications: Primarily aimed at sustainable aviation, including commercial jets, air taxis, and UAVs.
– Market Impact: Potential to significantly influence the push for green aviation technologies and comply with stringent environmental regulations.
– Comparison with Existing Solutions: It offers superior thermal management and propulsion efficiency compared to traditional jet engines and current electric propulsion systems.
– Technical Details: Innovative use of dual heat exchangers to maintain fuel cell temperature and enhance propulsion efficiency.