Filed by the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials on August 1, 2024, this patent describes an advanced ammonia generator using plasma technology.
The patent, formally referred to as the “Ammonia Generator Using Plasma,” elaborates on a system designed for efficient ammonia production through innovative processes involving plasma reactors.
Features and Improvements:
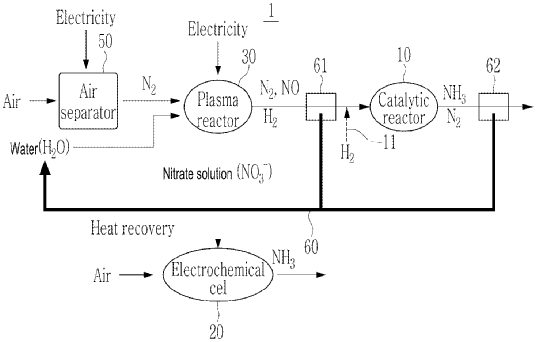
The key innovation in this patent lies in its use of plasma to facilitate chemical reactions that generate ammonia. Unlike traditional ammonia synthesis methods that typically involve high temperatures and pressures, this technology leverages a plasma reactor. The reactor uses nitrogen (N₂) as a discharge gas to create a plasma discharge. This plasma discharge then decomposes water (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂). Subsequently, nitrogen monoxide (NO) is produced from the nitrogen and oxygen mix. The entire process involves two reactors:
1. The first reactor, which synthesizes ammonia (NH₃) from nitrogen (N₂), nitrogen monoxide (NO), and hydrogen (H₂) produced by the plasma reactor.
2. The second reactor, which further converts nitrate solutions (NO₃⁻) generated in the plasma reactor to additional ammonia (NH₃).
Potential Applications:
This patented technology holds significant potential across various fields:
1. Agriculture: The efficient production of ammonia can be a boon for fertilizer manufacturing, reducing dependency on traditional methods.
2. Energy Storage: Ammonia can serve as an energy carrier, facilitating hydrogen transportation and storage.
3. Chemical Industry: The method can diversify the production routes for industrial chemicals that rely on ammonia as a precursor.
Technical Specifications:
According to the patent documentation, the plasma reactor operates by:
1. Generating a plasma discharge in a nitrogen atmosphere.
2. Decomposing water to produce hydrogen and oxygen.
3. Synthesizing nitrogen monoxide from the plasma-generated oxygen and nitrogen.
4. Feeding the synthesized gases into two sequential reactors for ammonia production.
By efficiently generating ammonia from basic components like nitrogen and water, it promises notable enhancements in energy efficiency and simplicity. While it holds potential for significant market impact, especially in agriculture and energy sectors, its success depends on overcoming scalability and economic feasibility challenges compared to existing technologies.