A recent patent introduced a novel hydrogen complex designed to enhance the functionality of steam turbine plants at nuclear power plants (NPPs). The patent, filed on June 21, 2024, outlines a comprehensive system intended to improve the efficiency of steam turbine operations, particularly those operating on wet steam with a consistent daily electric load.
Features and Improvements
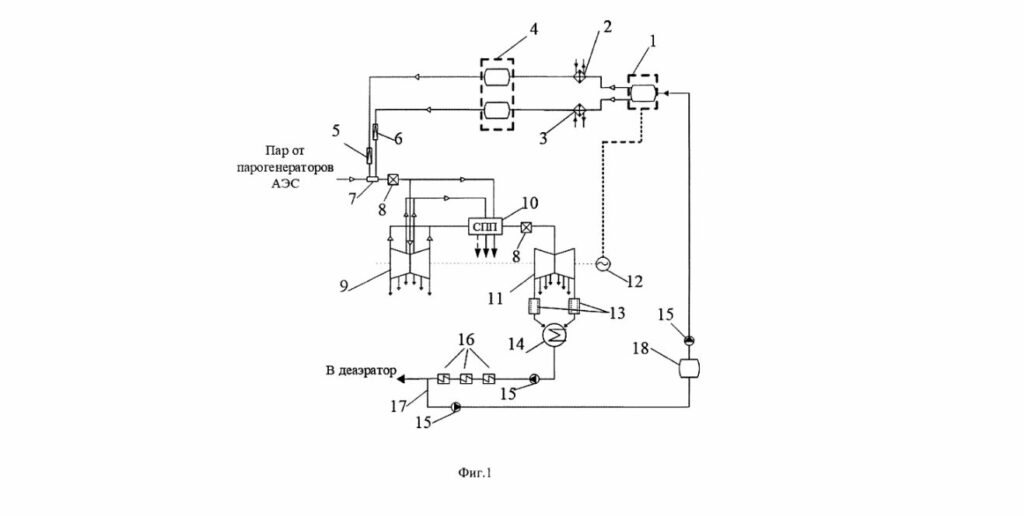
This hydrogen complex stands out due to its integration with the existing infrastructure of NPPs. The system is designed to produce hydrogen and oxygen via water electrolysis. Key components include intermediate coolers, storage systems, booster compressor plants, a hydrogen-oxygen combustion chamber, a magnetic separator, and catalytic recombiners for unreacted hydrogen. The process ensures the precise delivery of hydrogen and oxygen into a high-pressure storage system, which is then regulated and fed into the combustion chamber to superheat live steam within the steam turbine cycle.
Potential Applications
The patented technology primarily aims to improve the steam-turbine processes in NPPs, offering a more efficient solution for plants dealing with wet steam. By integrating this hydrogen complex, NPPs can achieve a more stable and higher-quality electrical output. Additionally, the system’s application could extend to other industrial settings where steam turbine efficiency is crucial.
Market Impact Analysis
By enhancing the reliability and efficiency of steam turbine operations, NPPs can achieve greater operational stability and potentially lower operational costs. This improvement may drive higher adoption rates of such technologies across the industry, encouraging further innovation and development.
Comparison with Existing Solutions
This patented hydrogen complex provides a more integrated and robust method for steam turbine efficiency compared to existing solutions. Traditional systems may not offer the same level of precision in managing hydrogen and oxygen flows or controlling the superheating process. Including components like magnetic separators and catalytic recombiners further distinguishes this system by addressing common issues related to unreacted hydrogen and system failures.
Technical Specifications and Processes
1. Hydrogen and Oxygen Production: Through water electrolysis
2. Intermediate Coolers: Utilized to manage the temperature of produced gases
3. Storage Systems: High-pressure setups for hydrogen and oxygen
4. Booster Compressors: Enhance the storage capabilities and manage pressure levels
5. Hydrogen-Oxygen Combustion Chamber**: Central to the superheating process
6. Magnetic Separator: Ensures purity and efficiency in the system
7. Catalytic Recombiners: Address unreacted hydrogen, improving safety and efficiency
Key Takeaways
– Efficiency Boost: Enhances steam-turbine cycles in NPPs by efficiently producing and utilizing hydrogen and oxygen.
– Integrated System: Combines several advanced components to improve reliability and reduce failure rates.
– Market Influence: Could spur significant advancements in nuclear power plant technology and operational efficiencies.
– Improved Safety: Features like magnetic separators and catalytic recombiners ensure safety and operational integrity.